Unplanned Downtime
To better simulate real-world equipment availability, unplanned downtime events can be modeled within simulation runs. These downtimes help assess the impact of unexpected delays on overall performance.
Modelling unplanned downtime consists of two key parts:
1️⃣ The first part, covered in this page, is where collections of downtime events are created, organised into containers called Sets.
2️⃣ The second part, covered in the Simualtion inputs, involves assigning these sets to specific equipment and specifying the expected amount of unplanned downtime.
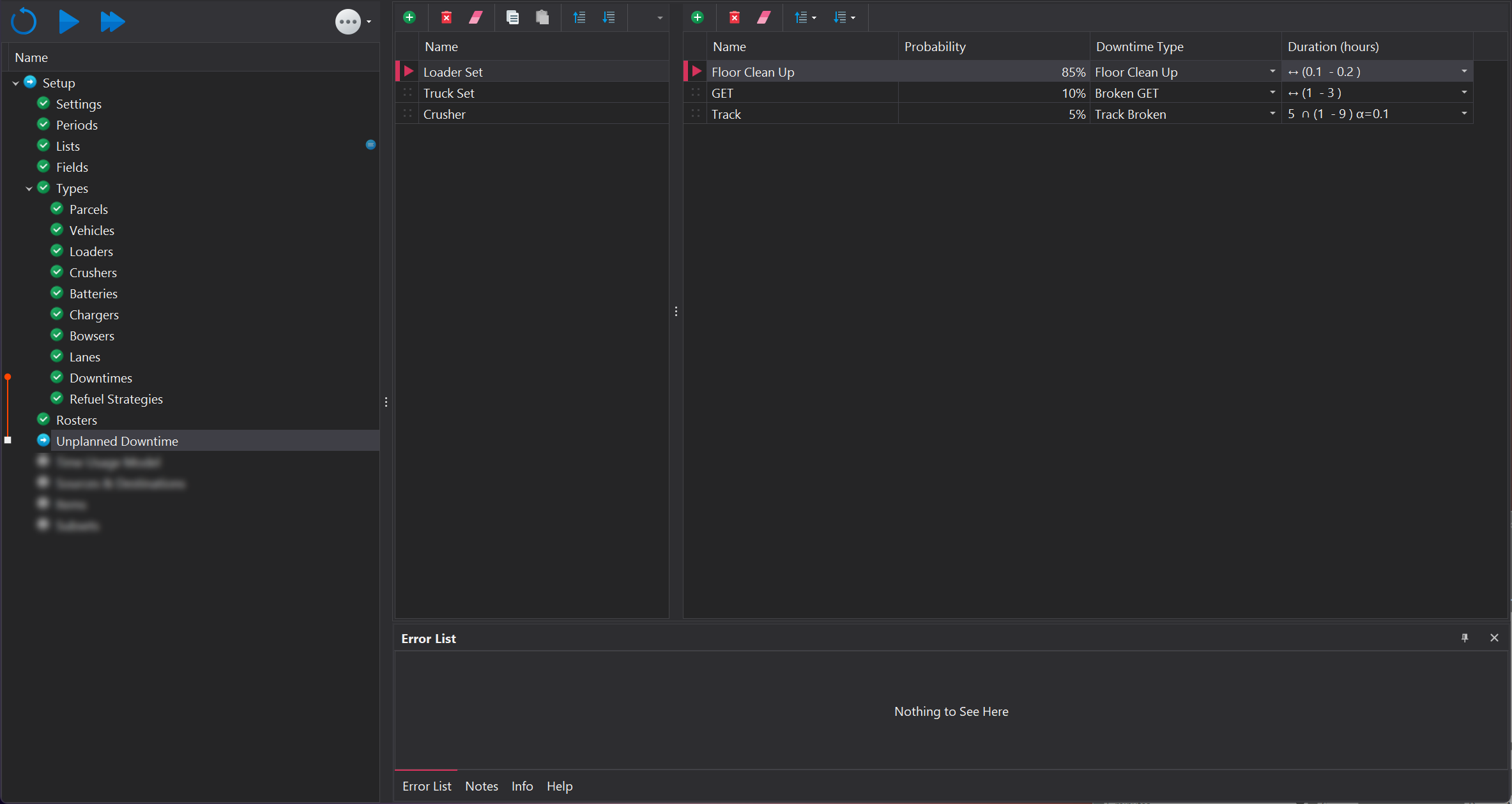
Unplanned Sets
An Unplanned Set is a collection of downtimes, each with an assigned probability of occurring. The cumulative value of all probabilities in the set must equal 100%. During the simulation, a random number is generated to determine which downtime event occurs: if the random number falls within the range assigned to a specific downtime, that event is selected. The higher the probabilty of that even occuring the more likely it is to be chosen due to it occupying a larger range.

Unplanned Downtimes
Unplanned downtime events must be added to Unplanned Sets, with entries easily managed through the toolbar at the top of the second panel. More information on the functions within the toolbar can be found in the Common User Controls page.
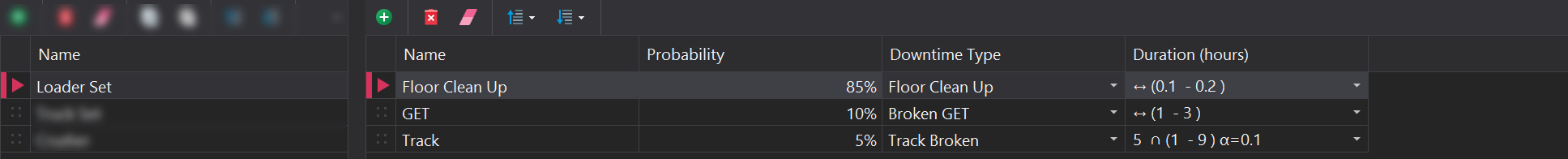
Each downtime entry in the set requires the following parameters:
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the unplanned event, which may differ from the assigned Downtime Type. |
| Probability | The likelihood of this downtime occurring. The cumulative probability of all downtimes must equal 100%. |
| Downtime Type | The assigned Downtime Type that the equipment will enter, selected from the list of events defined in the Downtimes step. |
| Duration | The duration of the downtime, in hours. This value can be represented by a probability distribution. More information about probability distributions can be found at the following link. |